Staining and Microbiologic Features:
- Gram-negative bacilli [1]
- It requires Factor X (hemin) for its growth [2]
- Factor V (NAD) is not necessary for its growth [1] . H. influenzae requires both factor V (NAD) and Factor X (hemin) for its growth and metabolic activity.[3]
- Haemophilus ducreyi grows on chocolate agar [1]
Virulence:
- Exotoxin is absent [4]
- Most strains of H.ducreyi can produce penicillinase (beta-lactamase), making them resistant to penicillin. [1]
- Initial infection does not confer permanent immunity against recurrent infection. [2]
Transmission:
- Sexual contact [5]
Diseases:
Chancroid: The patient can present with painful genital ulcers with unilateral tenderness and enlargement of inguinal lymph nodes (bubo). Ulcers are nonindurated and very painful. [1,6] Subsequent rupture of infected lymph nodes will release pus. [7]
Less common in the USA. [8]
How are genital lesions caused by H. Ducreyi different from those caused by other microorganisms?
- Patients with syphilis, caused by treponema pallidum, have painless ulcers with bilateral enlargement of inguinal lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are nontender and do not release pus. [7]
- Painful genital ulcers are also present in patients with herpes simplex infection. However, the affected patient also has systemic symptoms such as fever and muscle pain. [7]
- Patients with lymphogranuloma venereum, caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, have painless genital lesions with painful enlargement of lymph nodes. [9]
Diagnostic Testing:
- Culture [10]
- Staining of specimens obtained from genital ulcers or infected lymph nodes can show gram-negative coccobacilli [7]
- PCR [7]
References and Credits:
1 Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Seventeenth Edition 17th Edition by Warren Levinson, Peter Chin-Hong, Elizabeth A. Joyce, Jesse Nussbaum, and Brian Schwartz (page no: 213)
2 Jawetz, Melnick, & Adelberg’s Medical Microbiology Twenty-Seventh Edition (page no: 266)
3 Medical Microbiology by Patrick R. Murray Ph.D., Ken Rosenthal Ph.D., Michael A. Pfaller MD, 8th edition (page no: 244)
4 CMMRS edition 6, 2016-17 (page no: 100)
5 Medical Microbiology by Patrick R. Murray Ph.D., Ken Rosenthal Ph.D., Michael A. Pfaller MD, 8th edition (page no: 243)
6 Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Seventeenth Edition 17th Edition by Warren Levinson, Peter Chin-Hong, Elizabeth A. Joyce, Jesse Nussbaum, and Brian Schwartz (page no: 633)
7 CMMRS edition 6, 2016-17 (page no: 97)
8 Medical Microbiology by Patrick R. Murray Ph.D., Ken Rosenthal Ph.D., Michael A. Pfaller MD, 8th edition (page no: 246)
9 First A id for USMLE step 1, 2021 edition (page no: 184)
10 Medical Microbiology by Patrick R. Murray Ph.D., Ken Rosenthal Ph.D., Michael A. Pfaller MD, 8th edition (page no: 247)
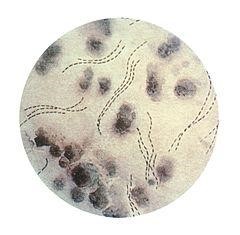
“ff haemophilus ducreyi” by isis325 is licensed under CC BY 2.0.
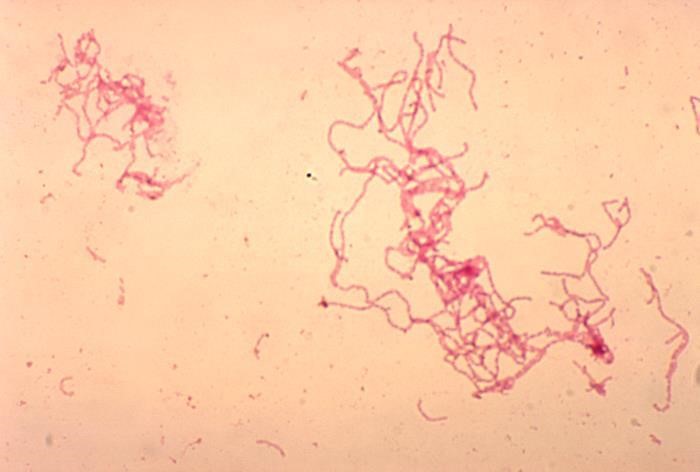
“2775 lores” by CDC/ Dr. Greg Hammond is marked with CC0 1.0.

